High Courts and Chief Justice of HC Important Questions for UPSC, SSC, and all other States Exams
About High Courts and chief Justice of HC
• In India, the Chief Justice of the High Court is appointed by President (After the consultation with the Chief Justice of India and the Governor of the State concerned)
• Articles 214-231 deal with the provisions of the High Courts in India.
• Article 217 deals with the appointment of judges.
• According to Article 222, the President may after consultation with the chief justice of India transfer a judge from one High Court to any High Court.
• Hight Court Judge sends his letter of resignation to the President.
• Oath and affirmation by governor of the state.
• The institution of high court originated in India in 1862 when the high courts were set up at Calcutta, Bombay, and Madras.
• Articles 214 to 231 in Part VI of the Constitution deal with the organization, independence, jurisdiction, powers, procedures, and so on of the high courts.
• Constitution does not specify the strength of a high court and leaves it to the discretion of the president.
• He holds office until he attains the age of 62 years.
• Calcutta High court is the oldest high court in India, it was established in the year 1862.
• In the same year, Bombay and Madras High court were established.
• Bombay, Madras, and Calcutta are the three chartered high courts in India.
• There are currently 25 high courts in India as of September-2020.
• Telangana and the Andhra Pradesh high courts are the newly-formed high courts of India, which were formed in the year 2019.
• Barnes Peacock was the first chief justice of the Calcutta High court, which assumed charge on 1 July 1862.
• Indian High Court Act was passed in 1861 during the period of Lord Canning.
• Bombay High Court: The high court’s jurisdiction extends to the states of Goa and Maharashtra, the Union Territories of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu.
• Calcutta High Court: West Bengal and the Union Territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
• Madras High Court: Tamil Nadu and the Union Territory of Puducherry.
• Gauhati High Court: Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, and Nagaland.
• Kerala High Court: Kerala and the Union Territory of Lakshadweep.
• Punjab and Haryana High Court: Punjab and Haryana, as well as the Union Territory of Chandigarh.
• The High Court has the most number of judges is the Allahabad High Court.
• Justice Rajesh Bindal is the current Chief Justice of Allahabad High Court.
• The first Indian to become the Chief Justice of High court – P. B. Chakravarthi (Calcutta High Court).
• The first Indian to become the judge of the High court – Sambhunath Pandit (Calcutta High Court).
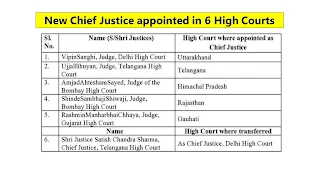
• The first woman Chief Justice of High court – Leila Seth (Himachal Pradesh).
• The first woman to become the judge of the High court – Anna Chandi (Kerala)
Let's Discuss Some Important MCQ on This Topic
Q.1 In India Chief Justice of High Court is appointed by
a) Central Government
b) State Government
c) Governor
d) President
Q.2. Which among the following is the oldest high court in India?
a) Bombay High Court
b) Madras High Court
c) Calcutta High Court
d) Allahabad High Court
Q.3. The age of retirement of a High Court Judge is
a) 65
b) 60
c) 58
d) 62
Q.4. The jurisdiction of which of the following high courts extends to the Union Territory of Lakshadweep?
a) Kerala
b) Tamilnadu
c) Bombay
d) Delhi
Q.5. The High Court has the jurisdiction under Article 226 for the enforcement of
a) Civil Rights
b) Fundamental Rights
c) Sanctioning Rights
d) Child Rights
• A High Court is empowered to issue directions, orders, or writs for the enforcement of a Fundamental Right and for any other purpose those include:
• Habeas corpus, Mandamus, Prohibition, Quo warranto,Certiorari.
• Habeas corpus - A writ of habeas corpus is used to bring a prisoner or other detainee before the court to determine if the person’s imprisonment or detention is lawful.
• Mandamus - It is a judicial writ issued as a command to an inferior court or ordering a person to perform a public or statutory duty.
• Prohibition - This writ is often issued by a superior court to the lower court directing it not to proceed with a case that does not fall under its jurisdiction.
• Quo warranto - It a writ or legal action requiring a person to show by what warrant an office or franchise is held, claimed, or exercised.
• Certiorari - A type of writ, by which an appellate court decides to review a case at its discretion.
Q.6. Ladakh is under the Jurisdiction of which High Court?
a) Jammu Kashmir
b) Himachal Pradesh
c) Punjab & Haryana
d) Uttarakhand
• Ladakh was declared as a union territory on 31st October 2019
• The Jammu and Kashmir High Court was established on 26th March 1928.
• The current chief justice of this high court is Gita Mittal.
Q.7. Election petitions regarding elections to the Parliament and State Legislatures can be filed before ________.
a) Election Commission
b) Supreme Court
c) High Court
d) President
• Election petitions are filed in the High Court of the particular state in which the election was conducted.
• Therefore, only the High Courts have the original jurisdiction on deciding on election petitions.
Q.8. Which one of the following writs can be issued by a High Court to secure the liberty of an individual?
a) Mandamus
b) Quo warranto
c) Certiorari
d) Habeus Corpus
• It is a legal document that is issued by a Court that orders a person or entity to perform a particular act or to stop performing a specific deed.
Q.9. Which of the following High Courts has the largest number of Benches?
a) Delhi
b) Madhya Pradesh
c) Guwahati
d) Kolkata
• Apart from the Principal Seat, the High Court has 3 (three) outlying Benches ;
• Kohima Bench for the State of Nagaland
• Aizawl Bench for the State of Mizoram
• Itanagar Bench for the State of Arunachal Pradesh
Q.10. The pension of a retired High Court Judge is charged to the
a) Consolidated fund of India
b) Consolidated fund of state where he last served
c) Consolidated fund of different state where he has served
d) Contingency fund of India
Q.11. The salaries and allowances of the Judges of the High Court are charged to the
a) Consolidated fund of India
b) Consolidated fund of state
c) Contingency fund of India
d) Contingency fund of state
Q.12. Which High Court stated that the divorce, by saying ‘Talaq’ 3 times, is illegal?
a) Calcutta
b) Bombay
c) Allahabad
d) Punjab
• On 8 December 2016, the Allahabad High Court
observed in a ruling that the practice of instant triple talaq was unconstitutional and violated the rights of Muslim women
Q.13. What is the nature of the dispute of Babri Mosque/Ramjanambhoomi Case before Allahabad High Court?
a) Writ petition
b) Title suit
c) Claim for compensation
d) Judicial review petition
• A suit based on a title by ownership
Q.14. The mobile court in India is the brain child of
a) Justice Bhagwati
b) Rajeev Gandhi
c) Dr. A P J Abdul Kalam
d) Pratibha Patil
• First mobile court of India was launched in Haryana in 2007
Q.15. Name the Chairman of the ‘Law Commission’ who advocated that One-third of the Judges in each High Court should be from another State.
a) Justice P. N. Bhagwati
b) Justice Hidayatulla
c) Justice Chandrachud
d) Justice H. R. Khanna
Q.16. Which of the following High Court has become the first paperless court in the country?
a) Guwahati High Court
b) Kerala High Court
c) Bombay High Court
d) Odisha High Court




Thank you
ReplyDelete